
Human ear anatomy. Ears inner structure, organ of hearing ve (1000410
Ear Definition. The ear is the organ found in animals which is designed to perceive sounds. Most animals have some sort of ear to perceive sounds, which are actually high-frequency vibrations caused by the movement of objects in the environment. The human ear picks up and interprets high-frequency vibrations of air, while the sound-sensing.

Ear Labeled Diagram Anatomy Of The Ear Coloring Life Educations
This activity can be made easier by getting students to label the ear with a given list of keywords like the ones highlighted in bold below. Parts of the Human Ear. The pinna is a flap of skin and cartilage that collects sound waves and funnels them into the ear canal. The ear canal is a tube that connects the pinna to the eardrum.

Human Ear Anatomy Parts of Ear Structure, Diagram and Ear Problems
Human Ear Diagram Wondering what is the structure of the human ear, and how it performs the function of hearing? Look no further, this Bodytomy article gives you a labeled human ear diagram and also explains the functions of its different components. Home / Uncategorized / Human Ear Diagram

The human ear structure and how it works Connect Hearing
In this activity, students learn about the ear by exploring google slides and going to an interactive site that explores how the ear works.. Students use a simulation called "The Interactive Ear" which guides them though the outer, middle, and inner ear while explaining what each structure does. Students click through the virtual ear to label the diagrams and answer the question on the slides.
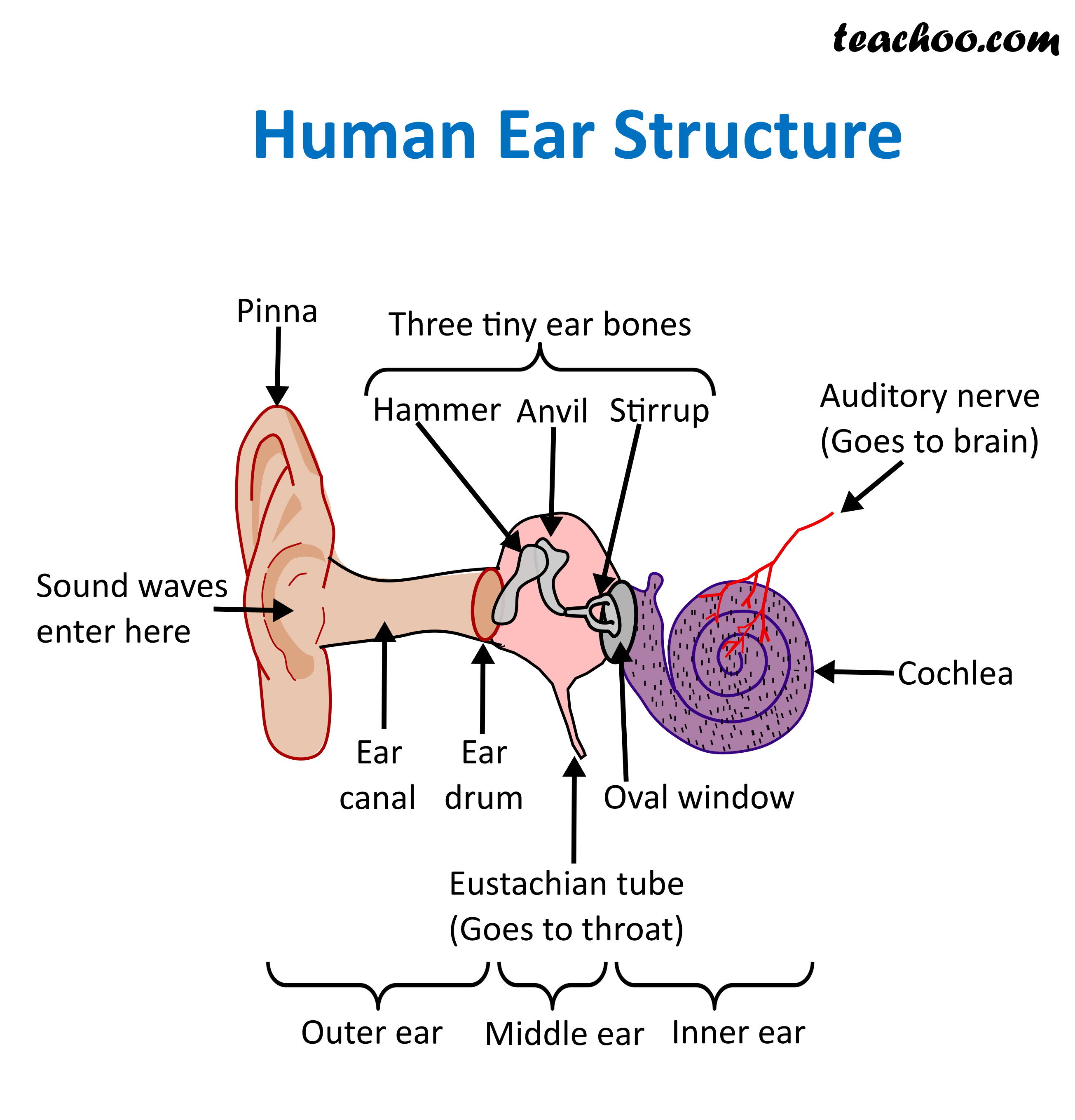
Structure and Function of Human Ear with Diagram Teachoo
1/4 Synonyms: External auditory meatus, External acoustic pore , show more. The ear is a complex part of an even more complex sensory system. It is situated bilaterally on the human skull, at the same level as the nose. The main functions of the ear are, of course, hearing, as well as constantly maintaining balance.
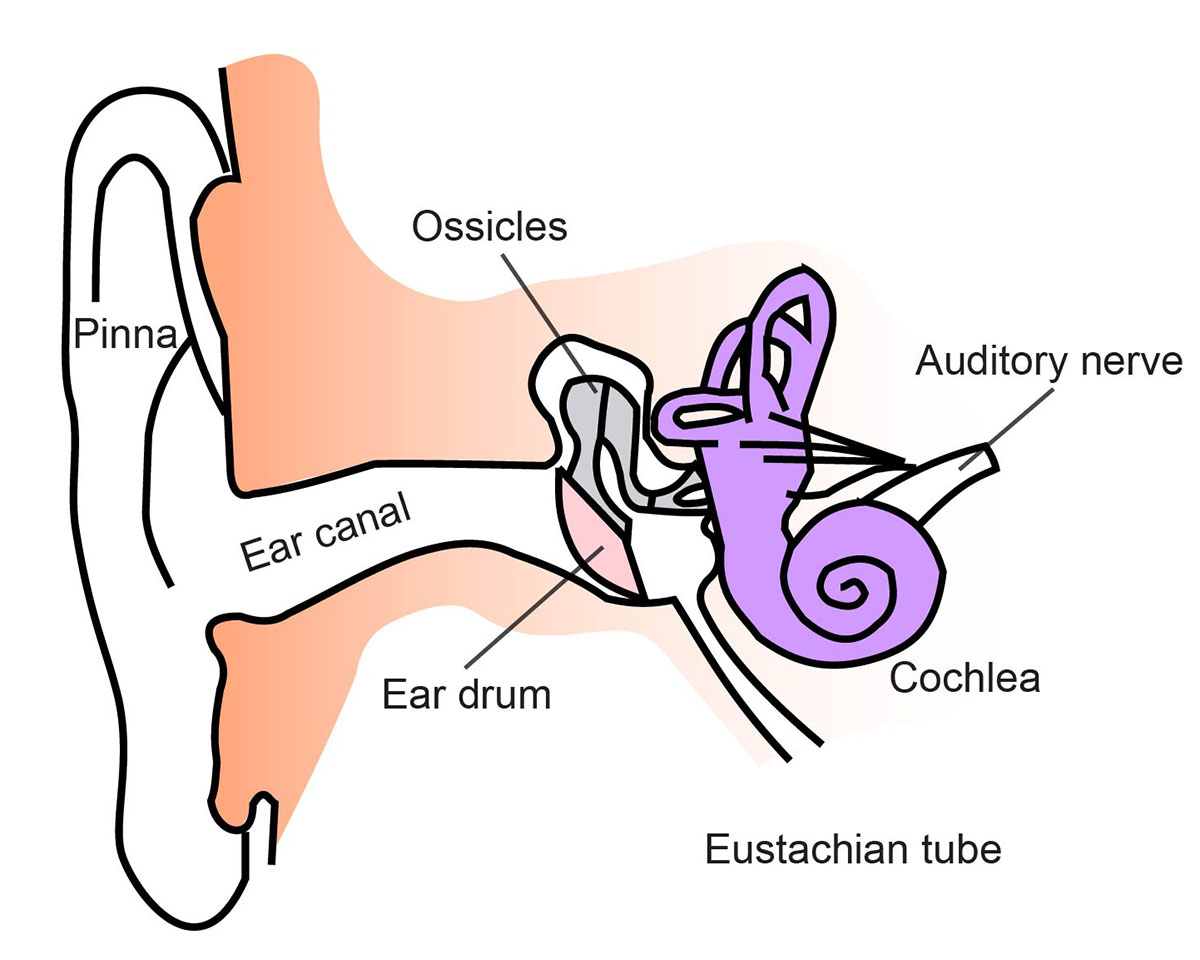
Hearing Sense Ask A Biologist
This fun and engaging Parts of the Ear Labelling Activity helps kids identify the different parts of an ear - ideal if you're teaching your class about the body, hearing and physical health. Learners must fill in the labels on the diagram with the appropriate names for each component. This resource is fully differentiated, meaning it comes in three different difficulty levels. This allows.

The Anatomy of the Outer Ear Health Life Media
Description: Structures of the Ear. The external ear contains the auricle, ear canal, and tympanic membrane. The middle ear contains the ossicles and is connected to the pharynx by the Eustachian tube. The inner ear contains the cochlea and vestibule, which are responsible for audition and equilibrium, respectively. English labels.
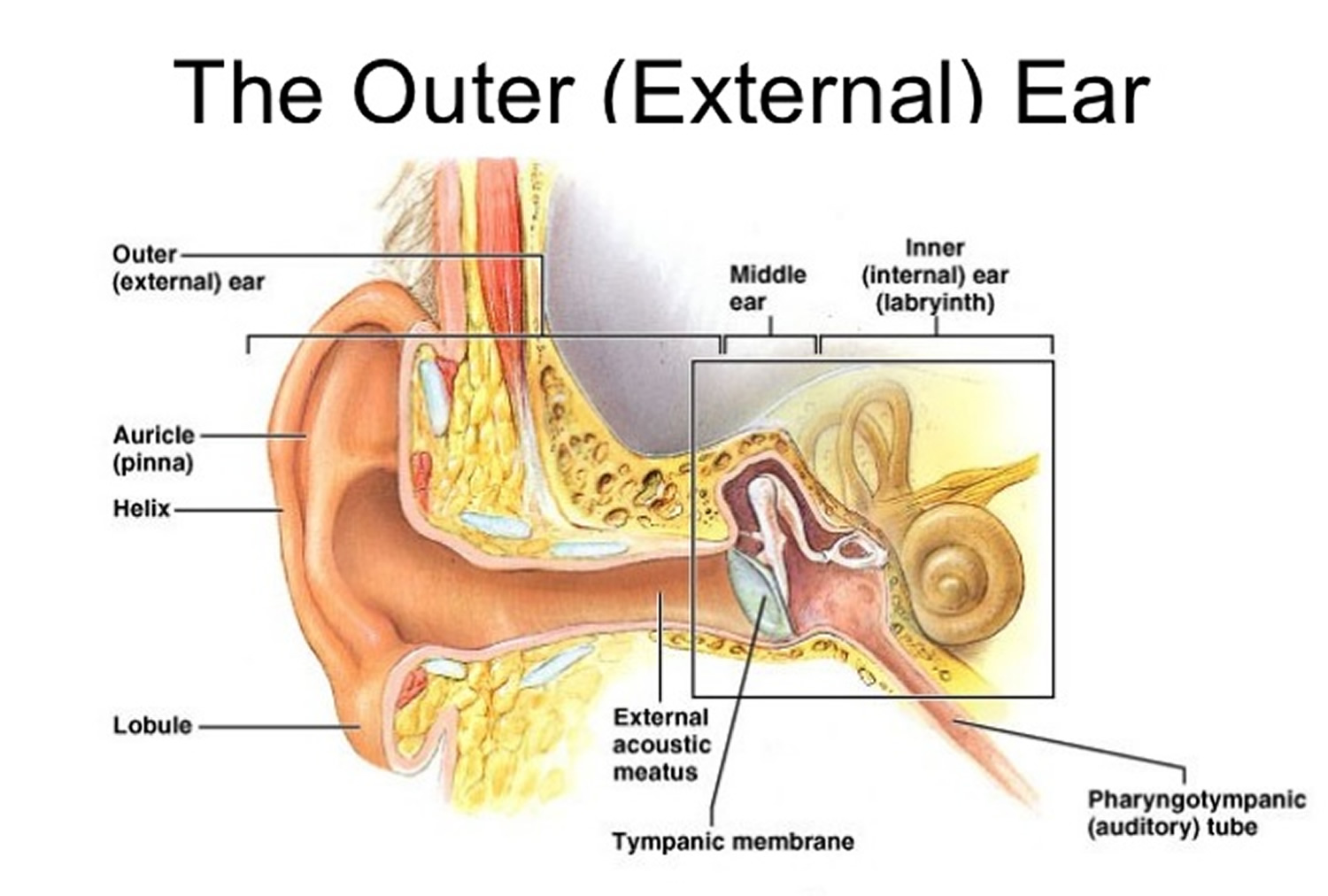
Outer Ear Anatomy Outer Ear Infection & Pain Causes & Treatment
This fun and engaging Parts of the Ear Labelling Activity helps kids identify the different parts of an ear - ideal if you're teaching your class about the body, hearing and physical health. Learners must fill in the labels on the diagram with the appropriate names for each component. This resource is fully differentiated, meaning it comes in three different difficulty levels. This allows.
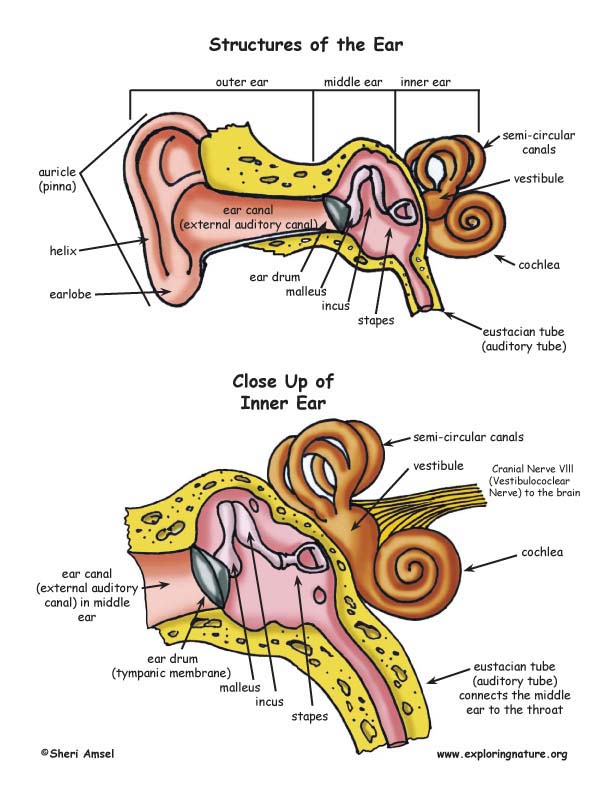
Structures of the Ear
3. hammer; first of the three auditory ossicles of the middle ear. tympanic membrane. 4. The eardrum. A structure that separates the outer ear from the middle ear and vibrates in response to sound waves. stapes. 5. the stirrup-shaped ossicle that transmits sound from the incus to the cochlea. semi-circular canals.
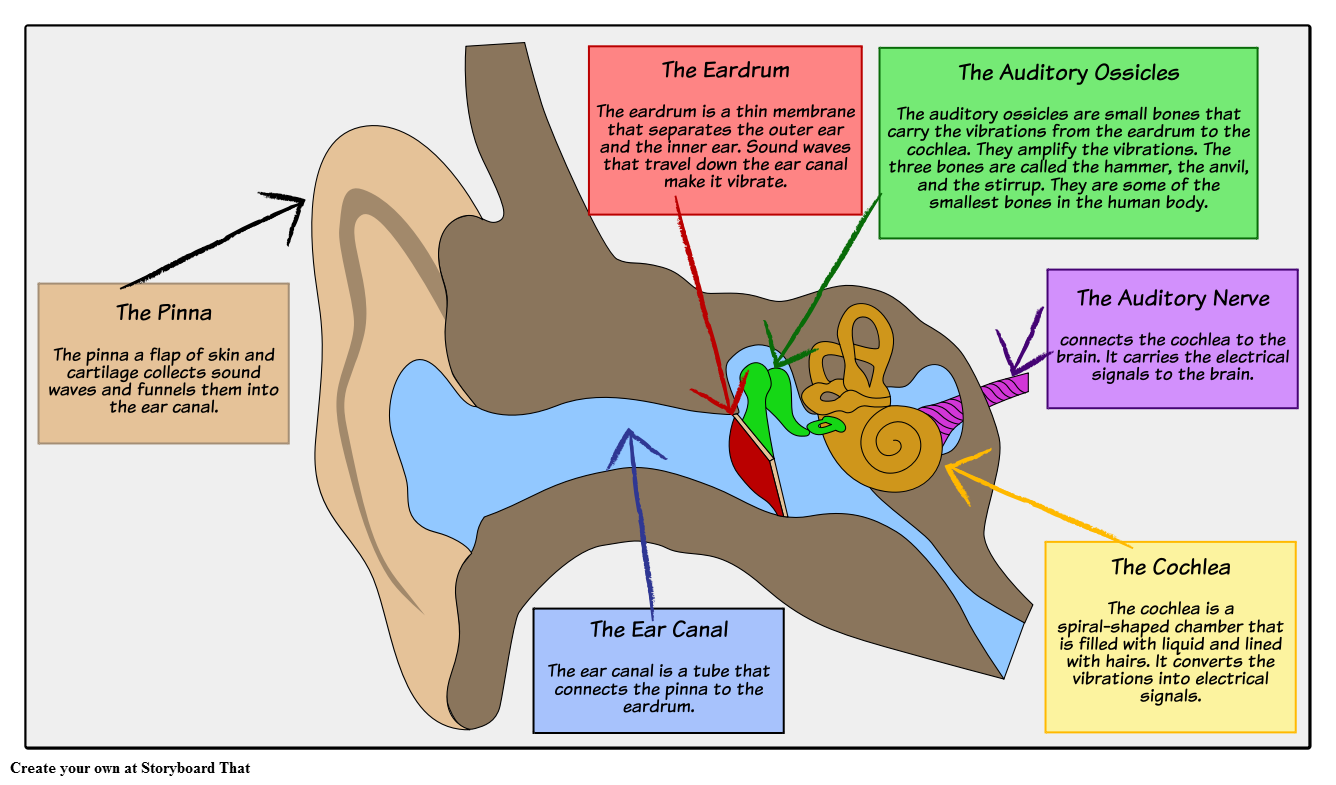
Structure of the Ear Diagram Activity
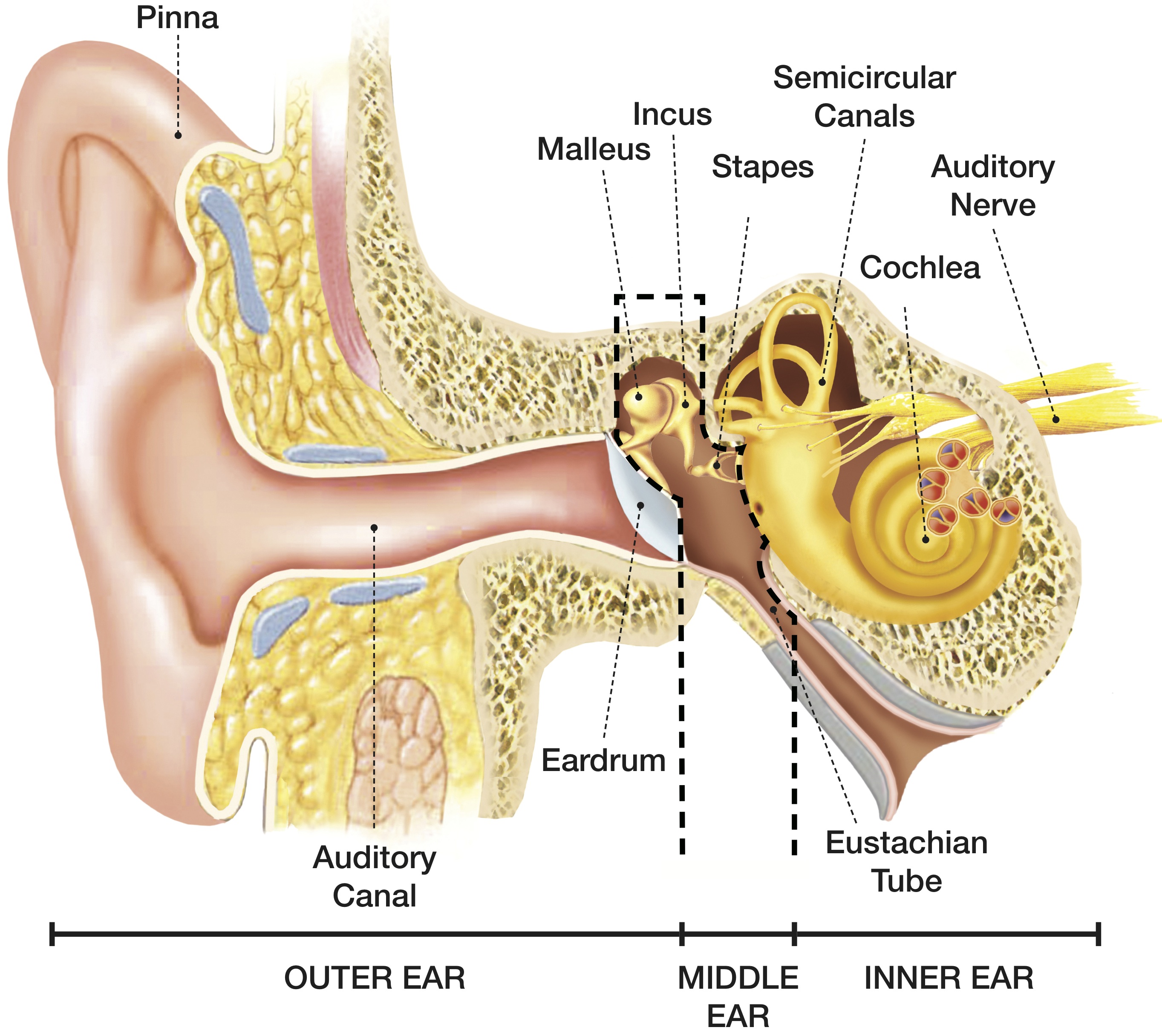
What are the parts of the ear? The three main parts of your ear include the outer ear, middle ear and inner ear. Your tympanic membrane (eardrum) separates your outer ear and middle ear. Outer ear (external ear)

1 A cross section of the human ear. Different parts of the ear can be
Helix: The outermost curvature of the ear, extending from where the ear joins the head at the top to where it meets the lobule. The helix begins the funneling of sound waves into the ear; Fossa, superior crus, inferior crus, and antihelix: These sections make up the middle ridges and depressions of the outer ear. The superior crus is the first ridge that emerges moving in from the helix.
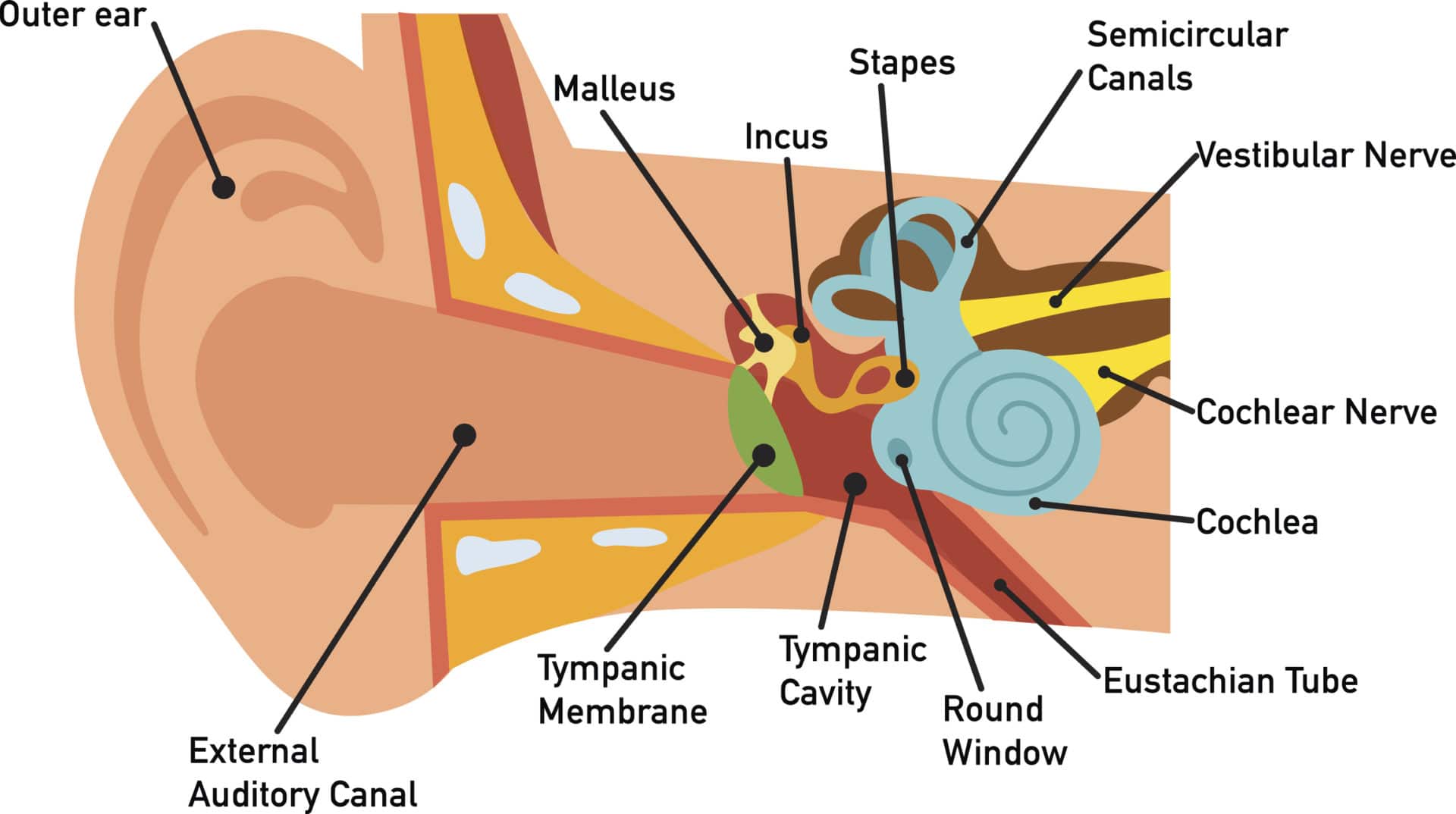
How You Hear Northland Audiology
Inner ear: The inner ear, also called the labyrinth, operates the body's sense of balance and contains the hearing organ. A bony casing houses a complex system of membranous cells. The inner ear.

Anatomy of the Ear [4]. Download Scientific Diagram
So as the air vibrates even the ear drum starts vibrating. Just like the skin of a drum. And as you can, the ear drum also separates the outer ear from the middle ear. This brings us to the middle ear. The middle ear consists of the three tiniest bones of the human body. And they're together the are called the ossicles. And they have pretty.

How The Ear Works
Human ear. The ear is divided into three anatomical regions: the external ear, the middle ear, and the internal ear (Figure 2). The external ear is the visible portion of the ear, and it collects and directs sound waves to the eardrum. The middle ear is a chamber located within the petrous portion of the temporal bone.
How We Hear Hearing Associates, Inc.
Take a moment to look at the ear model labeled above. This shows you all of the structures you've just learned about in the video, labeled on one diagram. Seeing them all together in this way is a great way to learn, since anatomical structures do not exist in isolation.
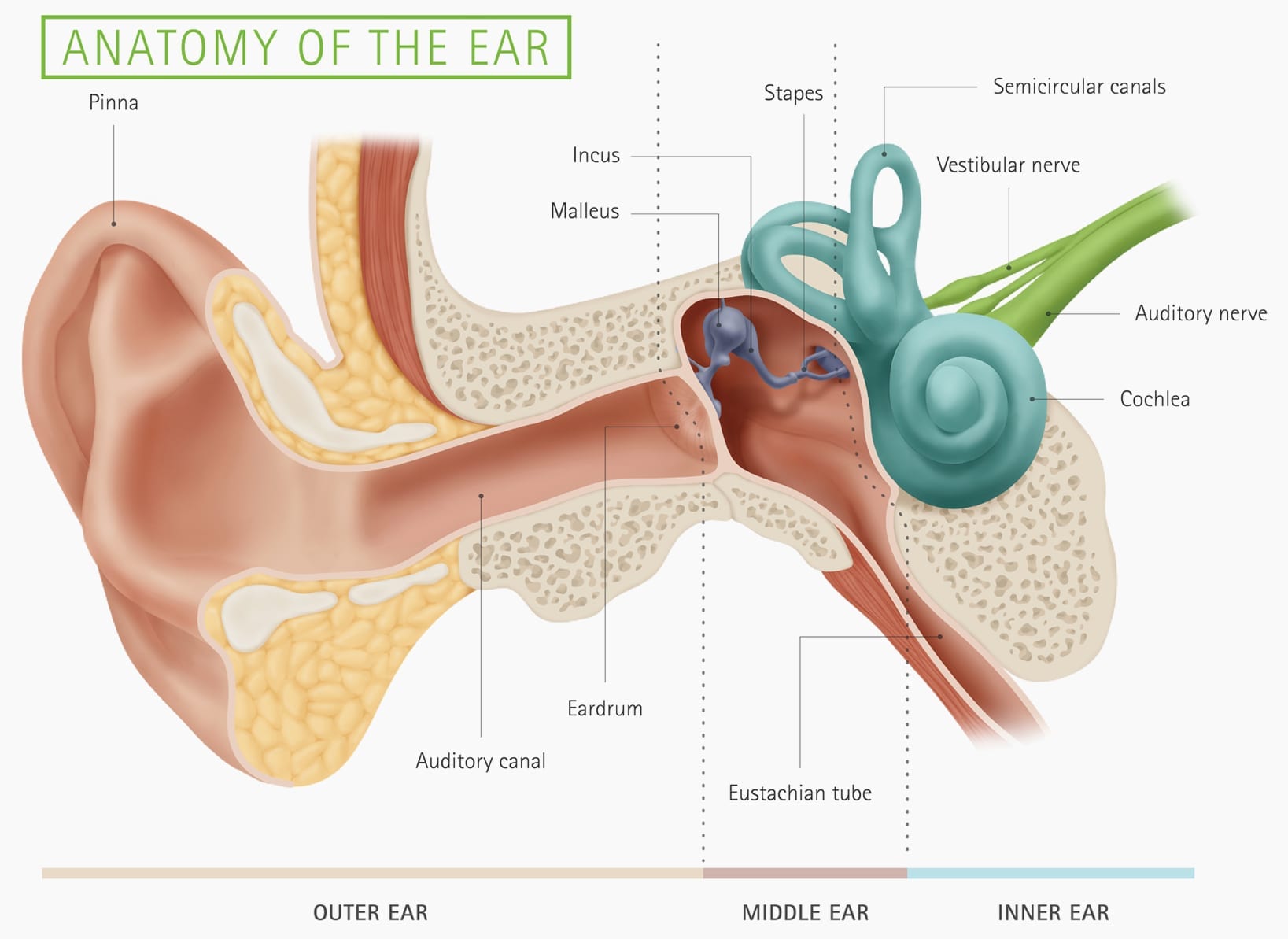
Your Hearing Heritage Hearing
human ear, organ of hearing and equilibrium that detects and analyzes sound by transduction (or the conversion of sound waves into electrochemical impulses) and maintains the sense of balance (equilibrium). Understand the science of hearing and how humans and other mammals perceive sound How humans and other mammals perceive sound.